By MATTHEW BROWN | Associated Press
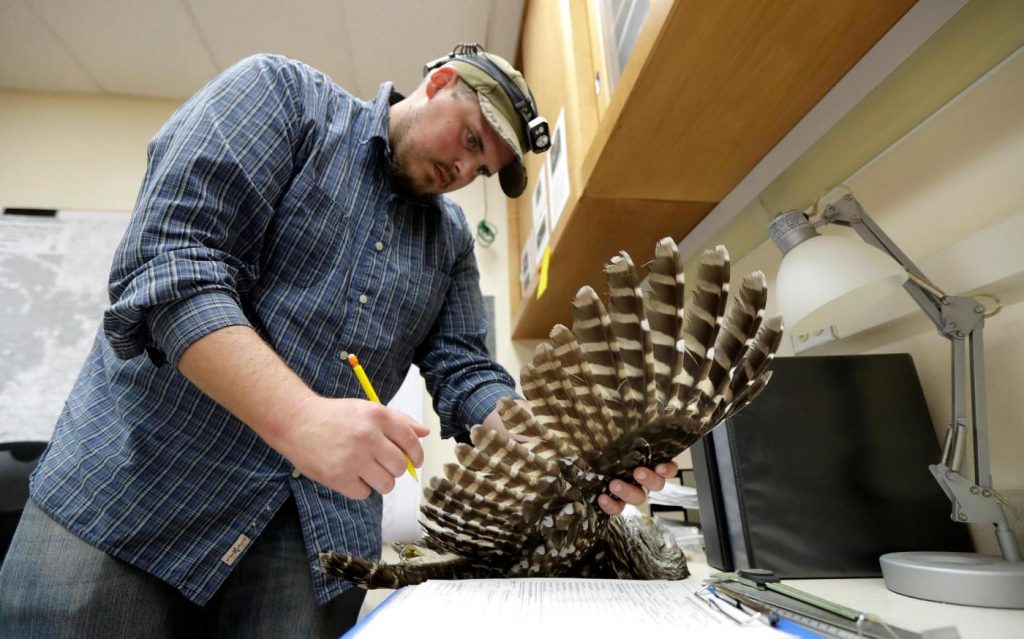
To save the imperiled spotted owl from potential extinction, U.S. wildlife officials are embracing a contentious plan to deploy trained shooters into dense West Coast forests to kill almost a half-million barred owls that are crowding out their smaller cousins.
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service on Wednesday was expected to release its final plan to prop up declining spotted owl populations in Oregon, Washington state and California. The Associated Press obtained details in advance.
The plan calls for killing up to 470,000 barred owls over three decades after the birds from the eastern U.S. encroached into the territory of two West Coast owls: northern spotted owls and California spotted owls. The smaller spotted owls have been unable to compete for food and habitat with the invaders.
RELATED: How to stop invasive owls from killing Bay Area owls — will new plan act fast enough?
Past efforts to save spotted owls focused on protecting the forests where they live. But the proliferation of barred owls in recent years is undermining that earlier work, officials said.
“We’re at a crossroads. We have the science that indicates what we need to do to conserve the spotted owls, and that requires that we take action on the barred owls,” said Bridget Moran, a deputy state supervisor for the Fish and Wildlife Service in Oregon.
The notion of killing one bird species to save another has divided wildlife advocates and conservationists. Some grudgingly accepted the proposal after a draft version was announced last year; others denounced it as reckless and a diversion from needed forest preservation.
Barred owls already are being killed in spotted owl habitats for research purposes, with about 4,500 removed since 2009, said Robin Bown, barred owl strategy leader for the Fish and Wildlife Service. Those targeted included barred owls in California’s Sierra Nevada region, where the animals have only recently arrived and officials want to stop populations from taking hold.
In other areas where barred owls are more established, officials aim to reduce their numbers but acknowledge shooting owls is unlikely to eliminate them entirely.
The new plan follows decades of conflict between conservationists and timber companies that cut down vast areas of older forests where spotted owls reside.
Early efforts to save the birds culminated in logging bans in the 1990s that roiled the timber industry and its political supporters in Congress.
Yet spotted owl populations continued to decline after barred owls first started showing up on the West Coast several decades ago.
Related Articles
Not just crossings, but also fencing, helps save California wildlife from being roadkill
Officers kill 3 coyotes at Golden Gate Park after attack on 5-year-old girl
Have allegations of horse racing abuse spoiled a July 4th tradition for Pleasanton friends?
Bay Area anchorman leaves television to rescue dogs, bears and bald eagles
Tahoe man won’t be charged for killing bear he said was in his kitchen
Opponents say the mass killing of barred owls would cause severe disruption to forest ecosystems and could lead to other species — including spotted owls — being mistakenly shot. They’ve also challenged the notion that barred owls don’t belong on the West Coast, characterizing their expanding range as a natural ecological phenomenon.
RELATED: Giving a hoot: How to protect owls in your backyard
“The practical elements of the plan are unworkable, and its adverse collateral effects would ripple throughout these forest habitats,” critics of the plan wrote in a letter earlier this year to Interior Secretary Deb Haaland that was signed by representatives of dozens of animal welfare groups.
Researchers say barred owls moved westward by one of two routes: across the Great Plains, where trees planted by settlers gave them a foothold in new areas; or via Canada’s boreal forests, which have become more hospitable as temperatures rise because of climate change.
Supporters of killing barred owls to save spotted owls include the American Bird Conservancy and other conservation groups.
“Our organizations stand in full support of barred owl removal as a necessary measure, together with increased habitat protections for all remaining mature and old-growth forests,” the groups said in comments on a draft proposal to remove barred owls that was released last year.
Northern spotted owls are federally protected as a threatened species. Federal officials determined in 2020 that their continued decline merited an upgrade to the more critical designation of “endangered.” But the Fish and Wildlife Service refused to do so at the time, saying other species took priority.
California spotted owls were proposed for federal protections last year. A decision is pending.
Under former President Donald Trump, government officials stripped habitat protections for spotted owls at the behest of the timber industry. Those were reinstated under President Joe Biden after the Interior Department said political appointees under Trump relied on faulty science to justify their weakening of protections.